In the ever-expanding realm of technology, where seamless connectivity is a necessity, the importance of cables and wire harnesses cannot be overstated. These silent heroes ensure the smooth transmission of data and power across various devices. Amidst this intricate network, the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standards play a crucial role, serving as a benchmark for wire sizes and capacities. In this blog post, we will delve into the significance of AWG standards in cables and wire harnesses, exploring their implications for performance, efficiency, and overall reliability.
“Ensuring reliable connections and efficient power flow, AWG standards in cables epitomize precision and uniformity, laying the foundation for a seamlessly interconnected world.”
Anonymous
Understanding AWG Standards
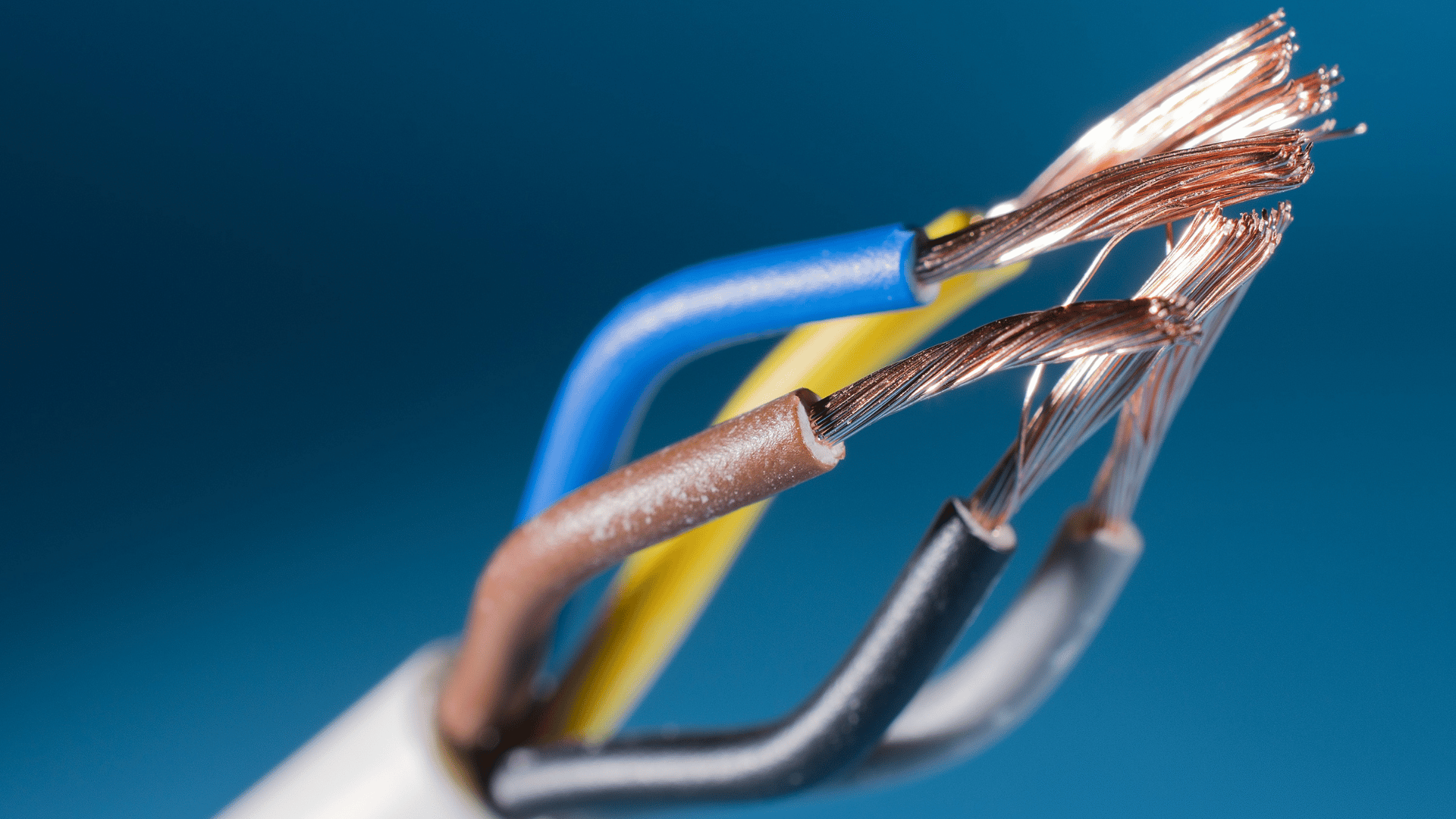
AWG standards, established by the American Wire Gauge system, are a set of guidelines that define the diameter and conductivity of electrical wires. In simpler terms, they provide a standardized way to measure and categorize the thickness of a wire, with a lower AWG number indicating a thicker wire. This standardized system ensures uniformity in wire manufacturing, aiding in the creation of reliable and compatible cable systems.
AWG in Cable Design
When it comes to cables and wire harnesses, the choice of wire gauge is critical. Different applications require different wire thicknesses to meet specific electrical and mechanical requirements. Thicker wires (lower AWG numbers) are capable of carrying more current over longer distances without significant voltage drop, making them suitable for power transmission. On the other hand, thinner wires (higher AWG numbers) are more flexible and ideal for applications where space is a constraint.
AWG and Signal Integrity
In the world of electronics, maintaining signal integrity is paramount. AWG standards play a pivotal role in achieving this by ensuring that the selected wire gauge can handle the required data transmission rates without signal degradation. Proper selection of wire gauge helps prevent issues such as attenuation and crosstalk, ensuring that the transmitted signals reach their destination with minimal distortion.
Temperature and AWG:
Temperature considerations are another crucial aspect of cable and wire harness design. AWG standards provide valuable information about a wire’s ability to withstand temperature variations. Cables operating in harsh environments or those carrying high currents may require thicker conductors with a lower AWG to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability.
AWG in Wire Harness Manufacturing
Wire harnesses, intricate assemblies of cables with connectors, are common in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. AWG standards play a key role in the manufacturing process of wire harnesses, guiding the selection of wires for specific functions within the assembly. This ensures that each wire within the harness meets the necessary electrical and mechanical requirements, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of the system.
As we continue to witness rapid advancements in technology, the demand for efficient and reliable connectivity solutions grows. AWG standards serve as a compass in the complex landscape of cables and wire harnesses, providing a standardized approach to wire sizing that is essential for seamless integration and optimal performance. Understanding and adhering to AWG standards empower engineers and designers to create robust and dependable cable systems that form the backbone of our interconnected world.