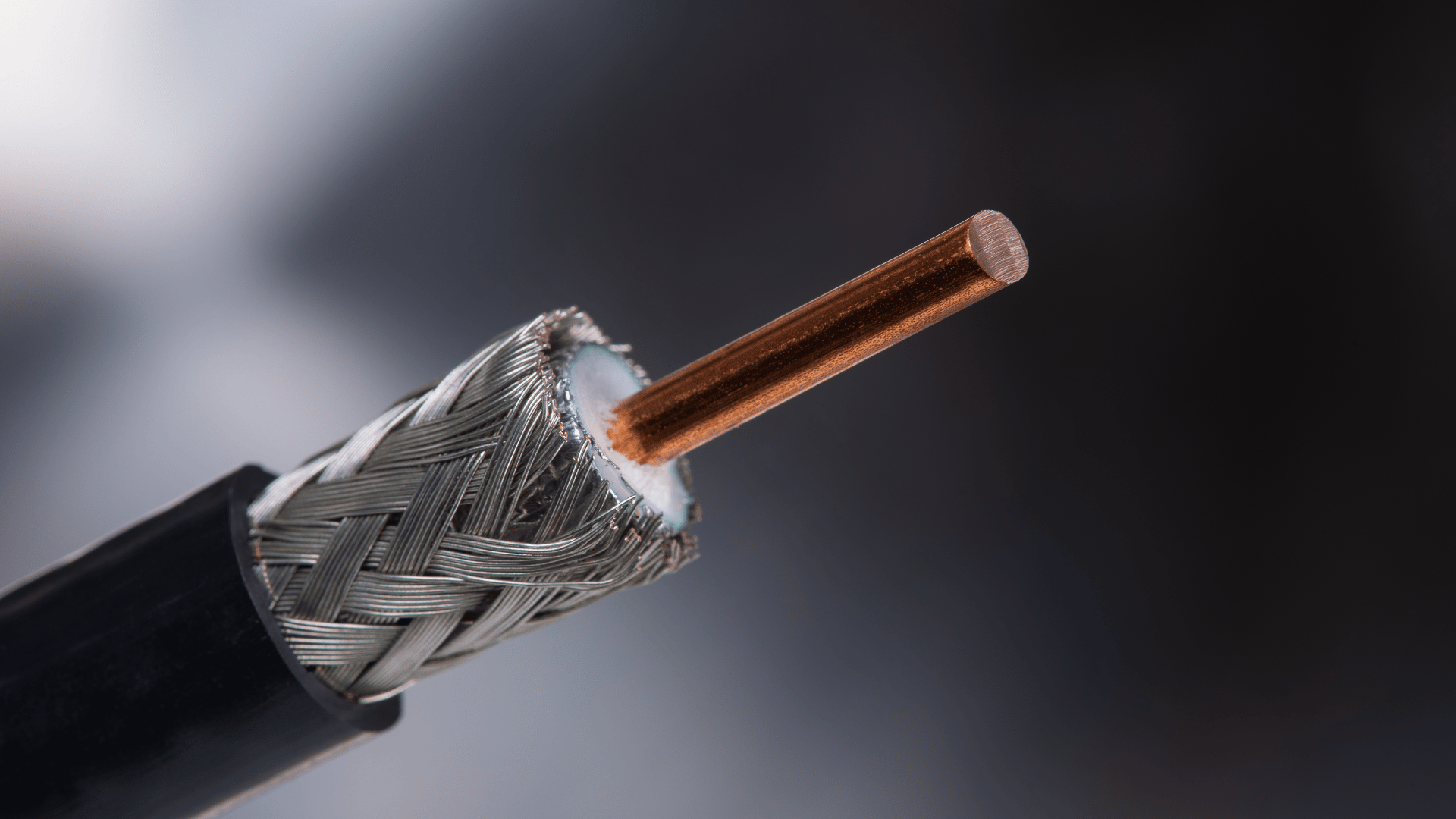In the world of electronics and connectivity, cables and cable harnesses play a crucial role in transmitting power and data from one point to another. Whether you’re setting up a home entertainment system, connecting devices in your office, or working on a complex industrial project, understanding the components of cables and cable harnesses is essential. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the key components that make up these essential tools for connectivity.
“Efficiency and quality go hand in hand when it comes to manufacturing cables and harnesses for the energy sector.”
Sarah Johnson – Lead Engineer at PowerLink Technologies.
Components of Cables and Wire Harnesses
-
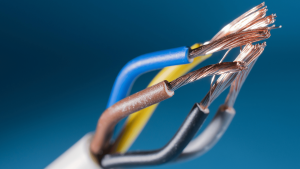
Conductors:
- Conductors are the heart of any cable. They are the wires responsible for carrying electrical signals or power. Conductors are typically made of materials like copper or aluminum, known for their excellent conductivity. The size and configuration of these conductors can vary based on the cable’s intended use.
-
Insulation:
- Insulation materials are used to protect the conductors from coming into contact with each other or the surrounding environment. Common insulation materials include PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PE (polyethylene), and Teflon, among others. The choice of insulation material depends on factors such as the cable’s application and environmental conditions.
-
Shielding (if applicable):
- Some cables, particularly those used in high-frequency or sensitive applications, feature shielding. Shielding helps protect the signals from interference or external noise. Common types of shielding include foil shielding, braided shielding, or a combination of both.
- Jacket:
-
- The jacket is the outermost layer of a cable. It provides mechanical protection, resistance to environmental factors like moisture, heat, and chemicals, and additional insulation. The jacket material can vary to suit the specific needs of the application and its operating environment.
-
Connectors:
- In cable harnesses, connectors are essential for interfacing with devices or components. Connectors come in various types, such as USB, HDMI, RJ45, D-sub, and many others, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Proper connectors ensure secure and reliable connections.
-
Labels or Markers:
- To aid in identifying individual wires within a cable harness, labels or markers are often used. These labels assist with proper connection and troubleshooting, making maintenance and repairs easier.
-
Strain Relief:
- Strain relief components are critical for protecting the cable or wires at points where they connect to connectors or other devices. They help prevent damage caused by bending or pulling forces, ensuring the longevity of the cable assembly.
-
Cable Ties or Lacing:
- Cable ties or lacing are used to bundle and secure multiple cables or wires within a cable harness. Proper cable management is essential for organization, safety, and tidiness.
-
Grommets or Boots:
- Grommets or boots are used to protect cable or wire entry or exit points in enclosures or panels. They offer strain relief and environmental sealing, ensuring the integrity of the cable connections.
The specific components and their configurations in a cable or cable harness can vary widely based on the intended application, environmental conditions, and electrical requirements. Different industries and applications may have their own standards and specifications for cable assembly.
Understanding these fundamental components of cables and cable harnesses is essential for choosing the right products for your specific needs. Whether you’re setting up a home entertainment system, establishing a network in your office, or tackling a complex industrial project, having a good grasp of these components will help ensure reliable and efficient connectivity.