In the world of telecommunications and networking, coaxial cables play a crucial role in transmitting data reliably and efficiently. One of the key features that make coaxial cables stand out is their high level of insulation. This insulation serves several important purposes, making coaxial cables the preferred choice for a wide range of applications.
The insulation in coaxial cables
First and foremost, the insulation in coaxial cables serves to protect the signal being transmitted from external interference. Coaxial cables are often used in environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) are prevalent. Without adequate insulation, these external factors could disrupt the signal, leading to data loss or corruption. The thick layer of insulation surrounding the inner conductor of a coaxial cable acts as a barrier, shielding the signal from such interference and ensuring that it reaches its destination intact.
Furthermore, the insulation in coaxial cables also helps to maintain the integrity of the signal over long distances. As signals travel through a coaxial cable, they encounter resistance, which can cause attenuation or weakening of the signal. Insulation helps to minimize this attenuation by reducing the loss of energy as the signal travels along the cable. This is particularly important for applications that require the transmission of signals over extended distances, such as cable television distribution networks or long-distance telecommunications links.
In addition to protecting against external interference and minimizing signal attenuation, the insulation in coaxial cables also provides mechanical strength and durability. Coaxial cables are often subjected to harsh environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, moisture, and physical stress. The high-quality insulation used in coaxial cables helps to safeguard against these factors, ensuring that the cable remains structurally sound and reliable over time.
Moreover, the insulation in coaxial cables contributes to their overall safety. By providing a barrier between the inner conductor and the outer environment, insulation helps to prevent electrical shocks and shorts, reducing the risk of accidents and damage to equipment.
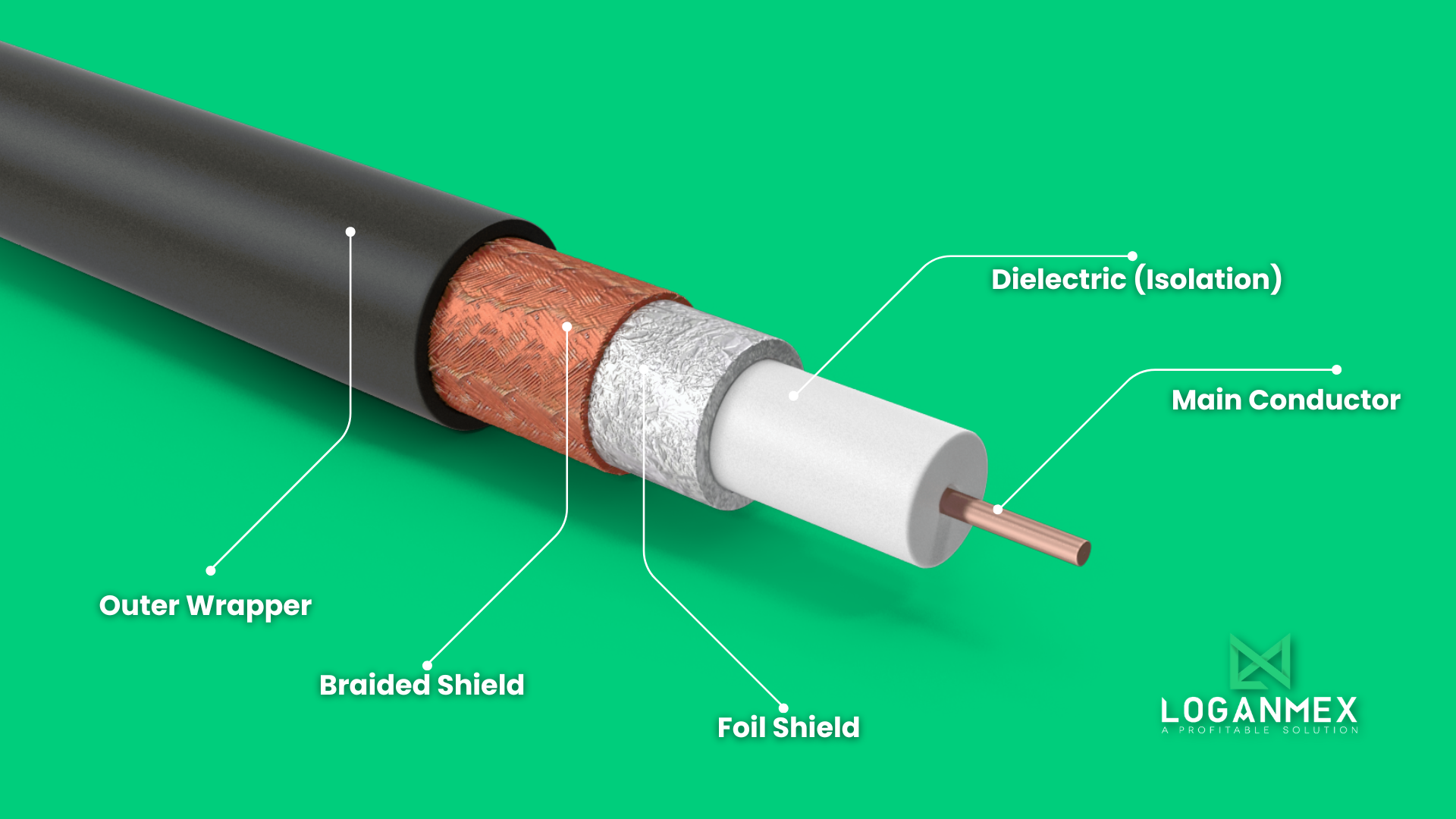
Dive into the Heart of Coaxial Cables
Let’s peel back the layers and explore the inner workings of these marvels of connectivity.
🔹 Outer Wrapper: The first line of defense. This protective layer shields the cable from physical damage and environmental hazards, ensuring durability and longevity.
🔹 Braided Shield: Beneath the outer wrapper lies the braided shield, a mesh-like structure made of conductive material. This shield acts as a barrier against electromagnetic interference, keeping your signals clear and uninterrupted.
🔹 Foil Shield: Another layer of defense against interference. The foil shield is a thin metallic layer wrapped around the inner components of the cable, providing additional protection from external disturbances.
🔹 Dielectric (Isolation): Nestled between the foil shield and the main conductor, the dielectric serves as an insulating barrier. Its primary function is to maintain the integrity of the signal by preventing electrical leakage and minimizing signal loss.
🔹 Main Conductor: At the core of it all, the main conductor carries the signal from point A to point B. Made of high-quality materials like copper or aluminum, this innermost layer ensures efficient transmission with minimal signal attenuation.